N-Queens II
Then-queens puzzle is the problem of placingn_queens on an_n×_n_chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
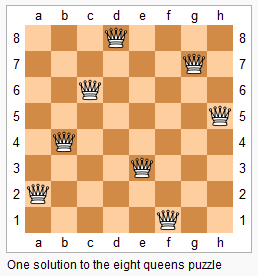
Given an integer n, return the number of distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Example:
Solution
The same as N-Queens, just need to output size of results.
Or just use a global variable
有关全局变量:
既然不需要输出最终解,也就省去了传递 rst 和把棋盘转成 String 的过程。一个问题是,如何在这种dfs + backtracking中维护一个 primitive type 变量,比如有效解的总数?
Java 中默认 primitive type 是 pass by value,而且 Integer type 虽然作为一个 object 存在但是是 immutable, 不能用来作为全局参数多个函数共同更新。
直接建全局变量太蠢了,也不好看。
Not using global variable
Last updated