Serialize and Deserialize N-ary Tree
Tree, Design
Hard
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize an N-ary tree. An N-ary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has no more than N children. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that an N-ary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
For example, you may serialize the following3-arytree
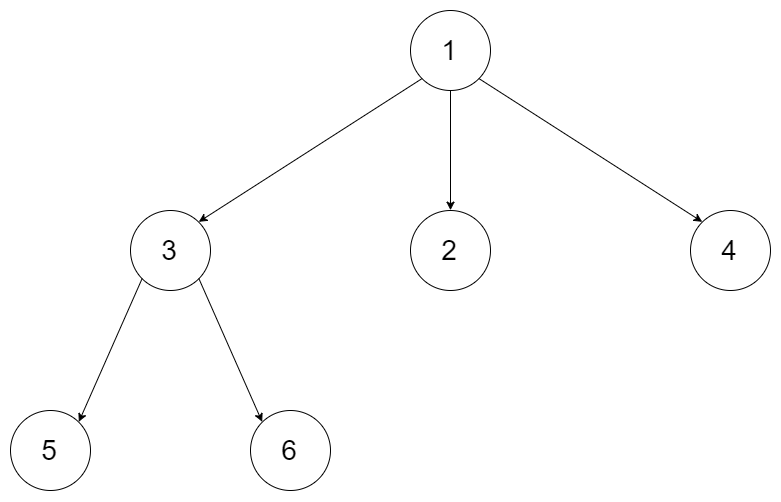
Image source: https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-n-ary-tree/
as[1 [3[5 6] 2 4]]. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Note:
Nis in the range of[1, 1000]Do not use class member/global/static variables to store states. Your serialize and deserialize algorithms should be stateless.
Solution
DFS - Recursion (Preferred)
和 Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree 很相似,同样可以用pre-order结合DFS来实现。
区别在于,在root value之后要append一个children count,这样才可以方便deserialize。
This is a template that can be applied to serialize and deserialize both binary and n-ary trees.
The only difference is that to serialize n-ary tree, we need to append the number of children of a node.
Serialize output with example as input:
--
Pre-order Depth-first search with Stack
example as input
serialize结果:
--
Reference
Last updated